Shortest-path ASP Narrative¶
Getting started¶
The framework is released as JAR file to be used on a Desktop platform, therefore it can be easily imported and used in any Narrative project.
The framework needs ANTLR4 library for its operation. You can download the JAR and include directly in your project or you can use Gradle or Maven.
Using EmbASP¶
In the following, we describe an actual usage of the framework by means of a running example; as a use case, we will develop a simple Desktop application to solve the shortest-path problem.
The complete code of this example is freely available here.
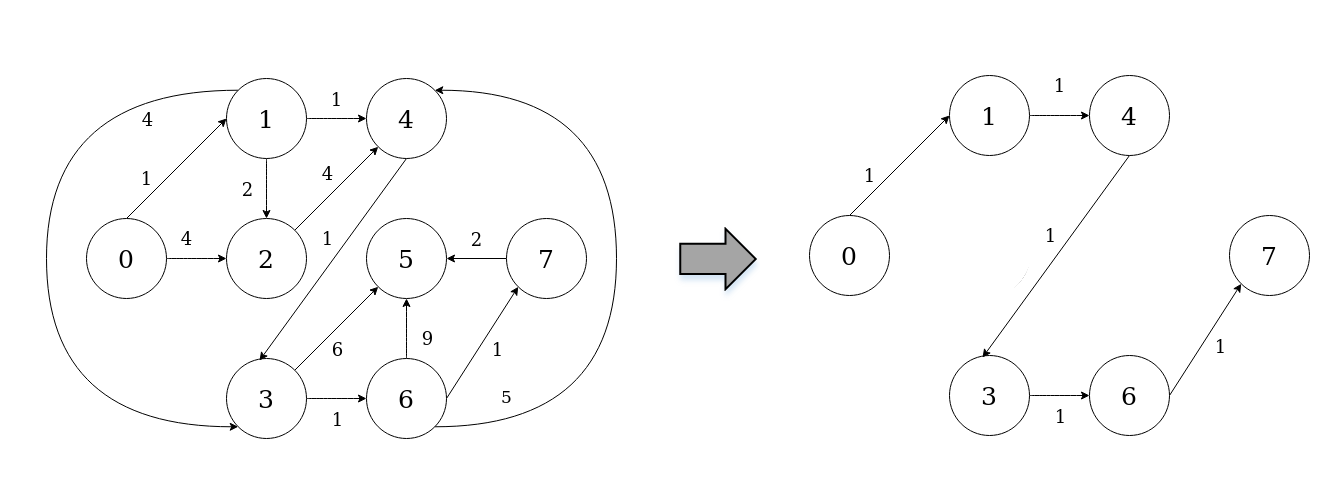
We will make use of the annotation-guided mapping, in order to create Narrative object constituting ASP predicates.
To this purpose, the following classes are intended to represent possible predicates that an ASP program can use:
@Id("edge")
public class Edge {
@Param(0)
private int from;
@Param(1)
private int to;
@Param(2)
private int weight;
public Edge(int from, int to, int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
[...]
}
@Id("path")
public class Path {
@Param(0)
private int from;
@Param(1)
private int to;
@Param(2)
private int weight;
public Path(int from, int to, int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
[...]
}
At this point, supposing that we have embedded the DLV2 solver in this project, we can start deploying our application:
public class ShortestPath {
private static int from, to; // source and destination node
private static ArrayList<Integer> sortedPath; // edges in the shortest path (sorted)
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Handler handler = new DesktopHandler(new DLV2DesktopService("executable/dlv2"));
ASPMapper.getInstance().registerClass(Edge.class);
ASPMapper.getInstance().registerClass(Path.class);
InputProgram input = new ASPInputProgram();
from = 0;
to = 7;
String rules = "from(" + from + "). to(" + to + ")."
+ "path(X,Y,W) | notPath(X,Y,W) :- from(X), edge(X,Y,W)."
+ "path(X,Y,W) | notPath(X,Y,W) :- path(_,X,_), edge(X,Y,W), not to(X)."
+ "visited(X) :- path(_,X,_)."
+ ":- to(X), not visited(X)."
+ ":~ path(X,Y,W). [W@1 ,X,Y]";
input.addProgram(rules);
for(Edge edge : getEdges())
input.addObjectInput(edge);
handler.addProgram(input);
AnswerSets answerSets = (AnswerSets) handler.startSync();
for(AnswerSet answerSet : answerSets.getOptimalAnswerSets()) {
ArrayList<Path> path = new ArrayList<Path>(); // edges in the shortest path (unsorted)
int sum = 0; // total weight of the path
for(Object obj : answerSet.getAtoms()) {
if(obj instanceof Path) {
path.add((Path)obj);
sum += ((Path)obj).getWeight();
}
}
join(from,path,sortedPath); // sorts the edges
print(sortedPath,sum); // shows the path
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static ArrayList<Edge> getEdges() {
ArrayList<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<Edge>();
edges.add(new Edge(0,1,1));
edges.add(new Edge(0,2,4));
edges.add(new Edge(1,2,2));
edges.add(new Edge(1,3,4));
edges.add(new Edge(1,4,1));
edges.add(new Edge(2,4,4));
edges.add(new Edge(3,5,6));
edges.add(new Edge(3,6,1));
edges.add(new Edge(4,3,1));
edges.add(new Edge(6,4,5));
edges.add(new Edge(6,5,9));
edges.add(new Edge(6,7,1));
edges.add(new Edge(7,5,2));
return edges;
}
[...]
}
The class contains an Handler instance as field, that is initialized with a DesktopHandler using the parameter DLV2DesktopService with a string representing the path to the DLV2 local solver.
The ASPMapper registers the classes created before in order to manage the input and output objects.
A string and a list of Edge representing facts, rules and constraints of the ASP program are added to an ASPInputProgram, and the ASPInputProgram is added to the Handler.
Finally the solver is invoked, and the output is retrieved.
The output predicates can be managed accordingly to the user’s desiderata. In this example the Path predicates, that represent the shortest path, are collected, sorted, and printed as well as the total weight of the path.
For further information, contact embasp@mat.unical.it or visit our website.